East West division of Himalayas
Kashmir Himalayas Kumaon Himalayas Nepal Himalayas Sikkim Himalaya Assam Himalayas
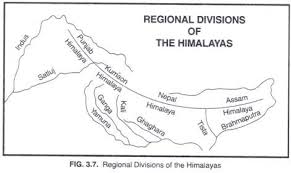
( Punjab Himalayas ) < [ satlaj – kali] < [ Kali – Kosi] < [ Kosi – Teesta] < [ Teesta- Dihang] [ Indus – sutlaj] (Brahmaputra)
Classification of Himalayas on the basis of Geographic Location
- Punjab Himalayas / Kashmir Himalaya / Himachal Himalaya→ Between the Indus and Sutlej
- Kumaon Himalayas→ Between Sutlej and Kali rivers
- Nepal Himalayas→ Between Kali and Tista rivers
- Assam Himalayas→ Between Tista and Dihang rivers
Kashmir Himalayas
- Karakoram , ladakh , Zaskar , Pir panjal , Dhaula dhar
- Kashmir Himalayas also known as Punjab Himalayas and Himachal Himalayas .
- Zozila pass situated between Kashmir and ladakh .
- In this region have many vallelies , Dun and lakes .
- The general elevation falls westwards.
- All the major rivers of Indus river system flow through Punjab Himalayas.
Kumaon Himalayas
- Kumaon Himalayas is Located in uttarakhand .
- The middle Himalayas discontinuous ranges are present between Great Himalayas and shiwalik – in western side called as Garwal Himalayas and in eastern side its called as Kumaon Himalayas .
- There are many peaks in this region like Nanda devi , Kamet , Badirinath , Kedarnath , Gangotri ( sourse of ganga) all peaks are found in southern side of Great Himalayas .
- After deposition lakes becomes dry .When lakes are dry it called as Tal and that dry lakes are very fertile so some cities are developed on these dry lakes like – Nainital , Bhimtal etc.
Nepal Himalayas
- Nepal Himalayas are the tallest section in all over the ranges in Himalayas .
- Higher peaks in Nepal himalayas –
- IN Great Himalayas—– Dhaulagiri , Annapurna , Mansalu , Evert , Makalu ( or kanchanjanga) .
- Kathmandu valley – There are many river sources , which cross to tibet region and meets India.
- Like Kali river ,Karnali river comes through India , Nepal border and meet into India called Ganga river.
- Gandak aries in Nepal near Kathmandu
- Kosi pass from Nepal and meet india in Bihar its also known as sorrow of bihar.
Sikkim Himalayas
- It’s a very small range Kosi to Teesta river.
- Peak : kanchanjanga
- Teesta is originated near kanchanjanga.
- There is a very important pass that is ‘Jelep la pass’. This pass is a trijunction of India- China- Bhuta.
Assam Himalayas
- Himalayas narrower .
- Lesser Himalayas close to great Himalayas. Because the shiwalik rangae are almost disappear in this region of Himalayas .
- There are important peaks like – Namcha Barwa , Kula kangrl.
- There is a pass also knoen as Diphu pass ,that pass is located on the India , China , Myanmar trijunction .
- Bengal Duar’s :- called Gateways of Himalayas, in this region uplifted in sudden way and it is very narrow.
- Duar’s are hilly , weightier regions and High rainfall. Tea cultivation happened In this regions.
“Duns” formation
- Dunis a valley between the Himalayan foothills and the Siwalik Range to the south .
- After lakes are dry out when river find weak rocks to cut across the mountain . dry rivers are called DUNS .
- Dehradun between Shiwaliks and Masoorie range.
Karewas ( of Kashmir)
- Karewas in Kashmir valley are some 367 meters thick.
- Flat-topped terraces of Kashmir valley on flanks of Pir panjal. This region are very fertile . this fertile land are made up of clay , sand from old deltaic fans.
- Now a days in this fertile land are use for cultivation of Apple , Saffron , Rice (stable food of kashmie).
Significance of Himalayas for India
| Strategic significance | Acts as a natural frontier of India with other countries (China, Pakistan, Afghanistan) |
| Climatic significance | Prevent further northward movement of summer monsoon and also prevent cold northern winds from Siberia to enter into India |
| Agricultural significance | Rivers from Himalayas deposits a lot of sediment on its foothold, from which are formed India’s most fertile agricultural grounds known as Northern plains |
| Economic significance | Huge hydro-electric power potential of Himalayan rivers + Himalayan timber + Himalayan Herbs & Medicinal plants |
| Tourism Significance | Comprises of Large ecological biodiversity, natural views & hill stations |